
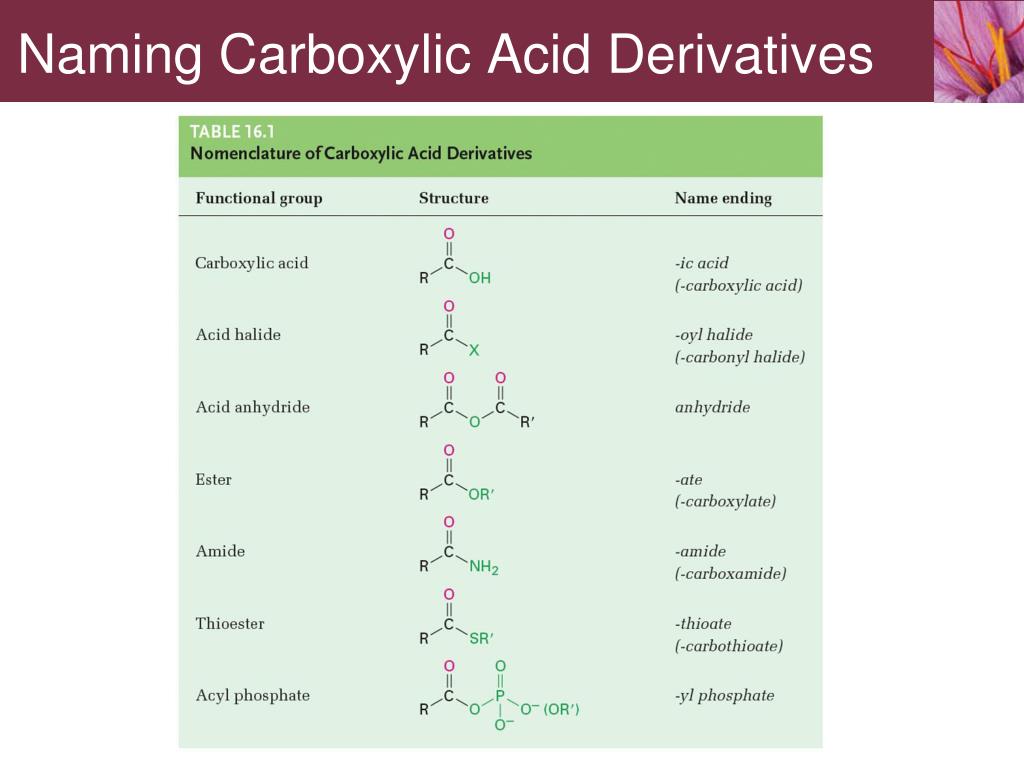
Esters (and Lactones) + H2O -> ? (acid-catalyzed vs.Relative Reactivities of Carboxylic Acid DerivativesĢ0-9 - Hydrolysis Reactions (Addition of H2O).Tetrahedral Intermediates, Reaction Rates, and Relative Stabilities.The Mechanism of Acyl Substitution Reactions Under Acidic Conditions.The Mechanism of Acyl Substitution Reactions Under Basic Conditions.
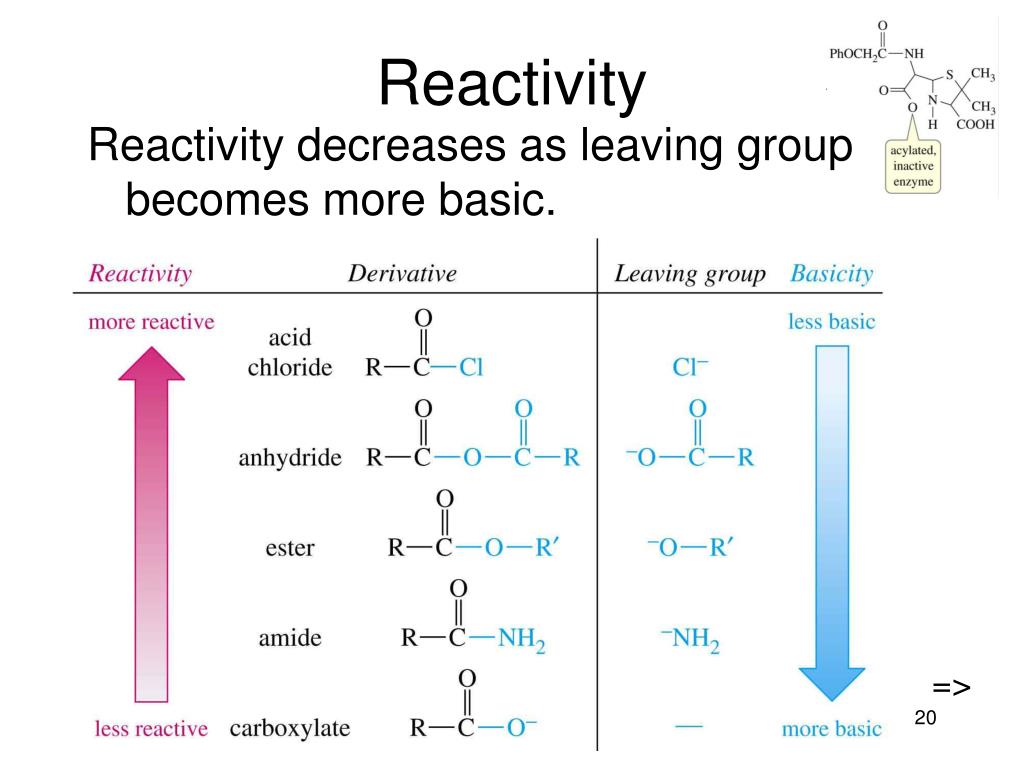
use pKa values to predict leaving group ability.
Reactivity of carboxylic acid derivatives free#
3 - Chemical Quantities and StoichiometryĤ - Types of Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometryħ - Quantum Mechanical View of the Atom, and Periodicityĩ - Covalent Bonding and Molecular Orbitalsġ0 - Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forcesġ5 - Applications of Acid-Base Equilibriaġ6 - Spontaneity, Entropy, and Free Energyġ8 - Transition Metals and Coordination ChemistryĢ0 - An Introduction to Organic Chemistryġ - Structural, Bonding, Molecular PropertiesĢ - The Nature of Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Cycloalkanesģ - Stereochemistry of Alkanes and Cycloalkanes: 3-D Structures of MoleculesĤ - The Study of Organic Reactions: An Overviewġ0 - Substitution (SN2, SN1) and Elimination (E2, E1) Reactionsġ1 - Mass Spectrometry and IR Spectroscopyġ3 - Conjugated Systems and UV Spectroscopyġ5 - Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (E.A.S.)ġ8 - Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition ReactionsĢ0 - Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution ReactionsĢ1 - Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution ReactionsĬarboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions - Section 20 of Organic Chemistry Notes is 27 pages in length (page 20-1 through page 20-27) and covers ALL you'll need to know on the following lecture/book topics:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
